We can compare adjectives by degrees. Adjectives come in a three-degree hierarchy: positive, comparative, and superlative.
Positive
It is an ordinary form of adjectives. We use the positive degree when referencing a single person, thing, or place.
A positive adjective is used to describe something without making any sort of comparison to anything else. For example, as seen in the sentence I am kind. or This is a great movie.
Examples
- The boy is smart.
- The small girl likes cake.
- Loki knows that hes tall.
Comparative
A comparative adjective is used in order to compare two things, it is quite often followed by the word than, you can see this in the following examples. I am nicer than him. or This movie is better than the first one.
When we describe two items or two individuals we use the comparative degree. Usually, we add the suffix -er to an adjective to produce this form. By adding -er to the word tall we get the comparative taller. If an adjective ends in y we must replace it with i before adding the suffix -er.
In addition, more placed in front of a descriptive word creates the comparative form.
Examples
- Freds party was more fun than Suzis.
- She is smarter than she thinks.
- Balto is taller than Merida.
Superlative
Indicates that the quality or quantity is at its highest or is most intense. A superlative adjective is used as a way of comparing more than two things and as a way to say that the thing you are talking about is the most, you might notice this in the following examples. I am the nicest of all the students. or This is the best movie out of the entire series.
We use the superlative degree when comparing three or more things. Adjectives in this form have the -est ending added to them. If an adjective ends in the letter y, it changes to i before adding the suffix. Like with the comparative degree, we can create the superlative degree by adding the word most.
Examples
- She is the smartest girl in the school.
- Robbi is the tallest when compared to his friends.
- She is more fun than the whole team combined.

Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Three Forms of Comparison of Adjectives in English
Positive: it is an ordinary form of adjectives
Comparative: shows when two persons or objects being compared
Superlative: indicates that the quality or quantity is at its highest or is most intense
- Comparative are used to describe people and things.
– My car is fast but Johnscar is faster.
– Emily is tall but Sophia is taller.
– I need a bigger car
- Than is used to compare one thing with another.
– Henry is older than Tom.
– Emily is smarter than Sophia.
– The second test was easier than the first one.
- The is used with a superlative:
– Where Are the Tallest Buildings in the World?
– Harry is the tallest student in this class.
- As…as is used to compare the attributes of two things that are equal
– Emily is as tall as Sophia.
– The first test is as easy as the second one.
General Rules in Forming Comparison of Adjectives

There are basic rules in forming the degrees of comparison:
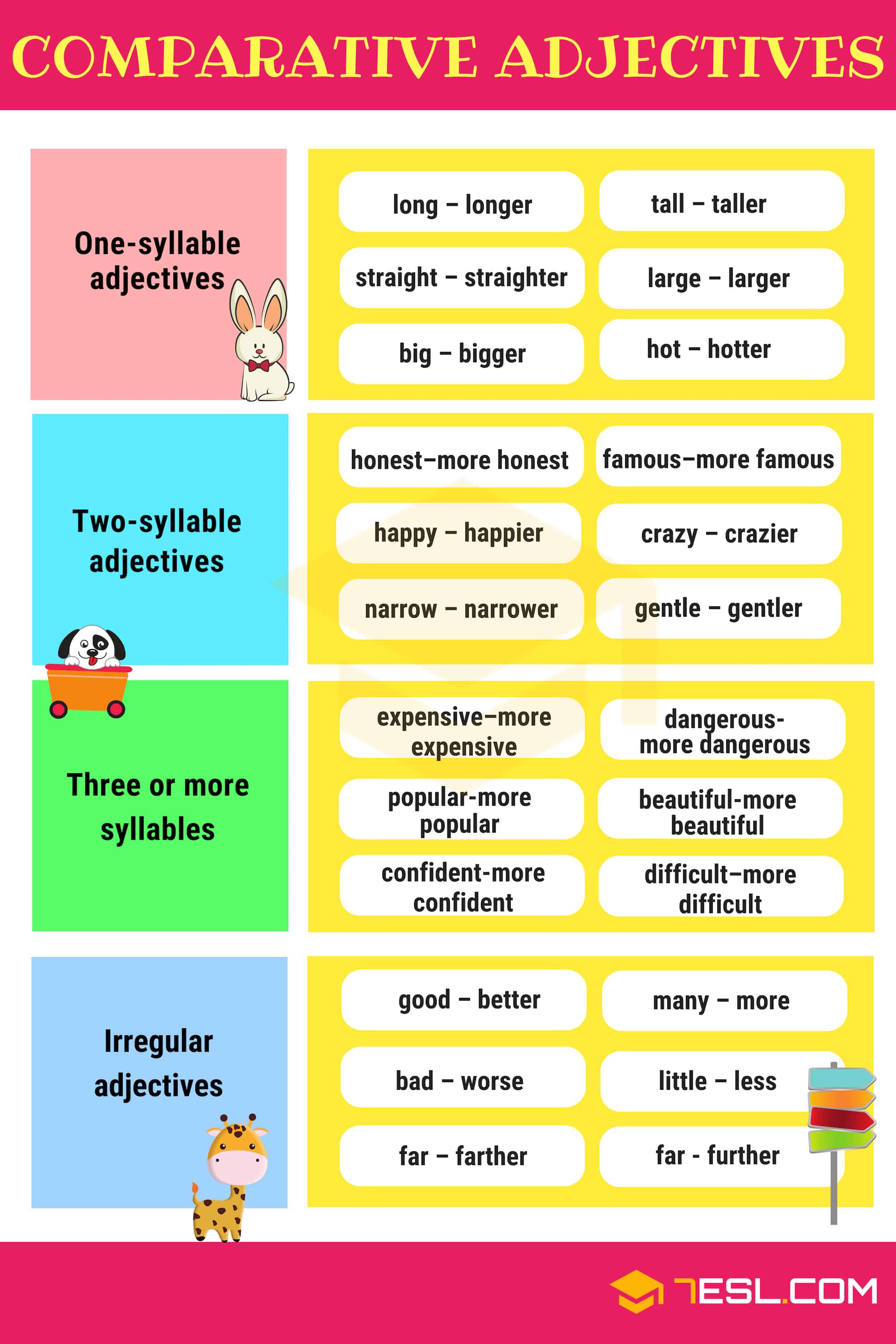
- For one-syllable adjective, add -er to form comparative and -est for superlative.
Examples:
- clear / clearer / clearest,
- dark / darker / darkest
- For most two-syllable adjectives, add -er for comparative and – est for superlative.
Examples:
- simple / simpler / simplest,
- gentle / gentler / gentlest
- For three or more syllables, always use more and most to form the comparative and superlative.
Examples:
- creative / more creative / most creative
- Some adjectives end with a consonant letter y, change y to I and add -er or -est.
Examples:
- busy / busier / busiest,
- merry / merrier / merriest
- Some adjectives end with a single vowel and single final consonant letter. Double the final consonant and add -er/-est.
Examples:
- thin / thinner / thinnest,
- fat / fatter / fattest
- When the adjectives end in e, add -r for the comparative and -st for superlative
Examples:
- wise / wiser / wisest,
- simple / simpler / simplest
- Irregular comparisons of adjectives are compared irregularly
Examples:
- good / better / best
- ill / worse / worst
Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Comparatives
Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Superlatives

Comparison of Adjectives: Forming Equative, Comparative and Superlative Adjectives

Notes for Irregular Comparison of Adjectives
(Exceptions)
Irregular Comparisons:
- Far / Farther than / the Farthest
- Far / Further than / the Furthest
Farther and Farthest generally refer to distance
Further and Furthest also refer to distance but they may have the meaning of additional
His voice carried farther than mine.
Further analysis of the data is needed.
- Old / Older than / the Oldest
- Old / Elder than / the Eldest
Older and Oldest refer to persons or things;
Elder and Eldest can only be used for members of the same family
My elder sister is a doctor.
The older generation doesnt like pop music.
but Elder cannot be placed before Than so Older is used:
Henry is my elder brother; he is two years older than I.